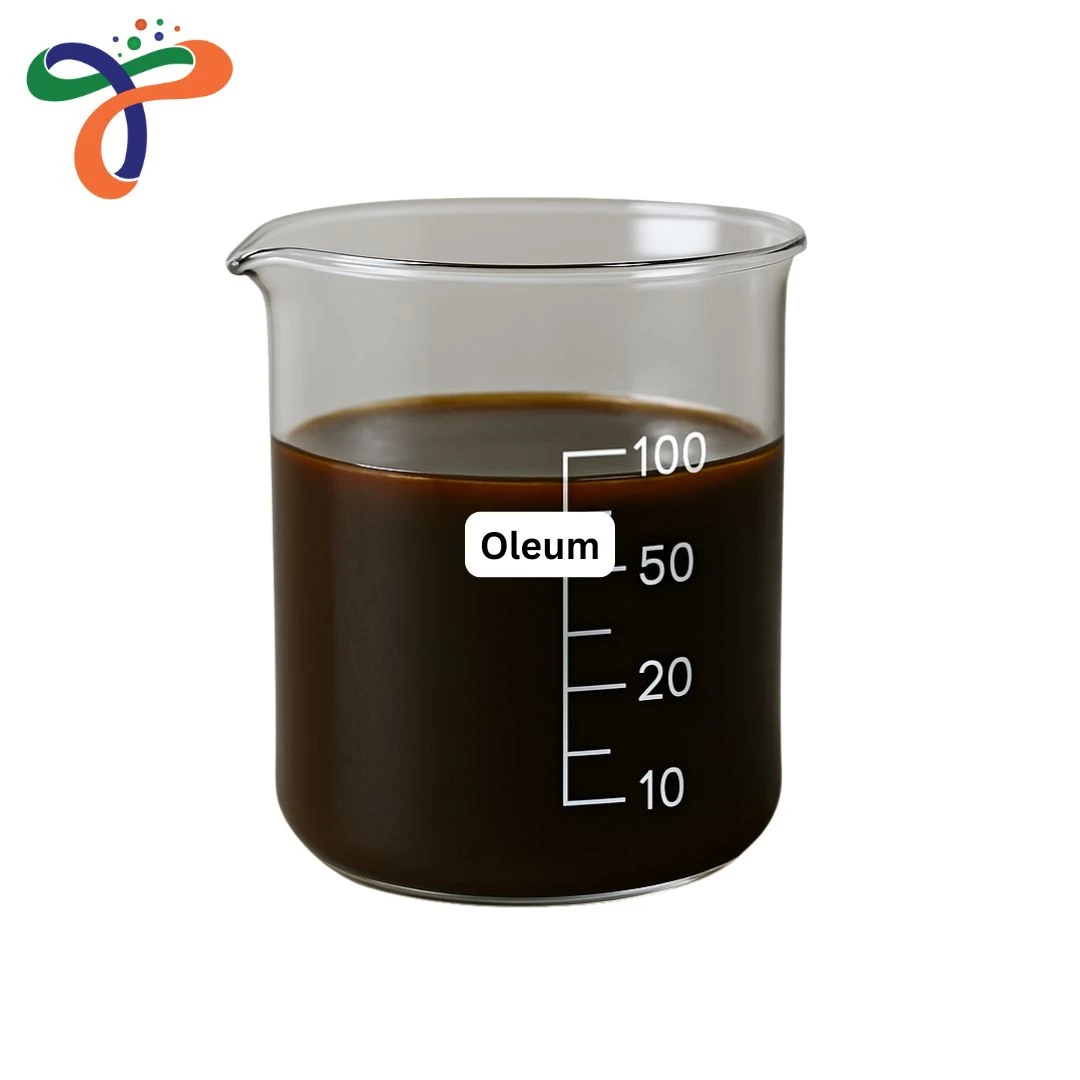
Oleum | 8014-95-7
Cas No :
8014-95-7
Form :
Liquid
Molecular Weight :
178.14 G/Mol
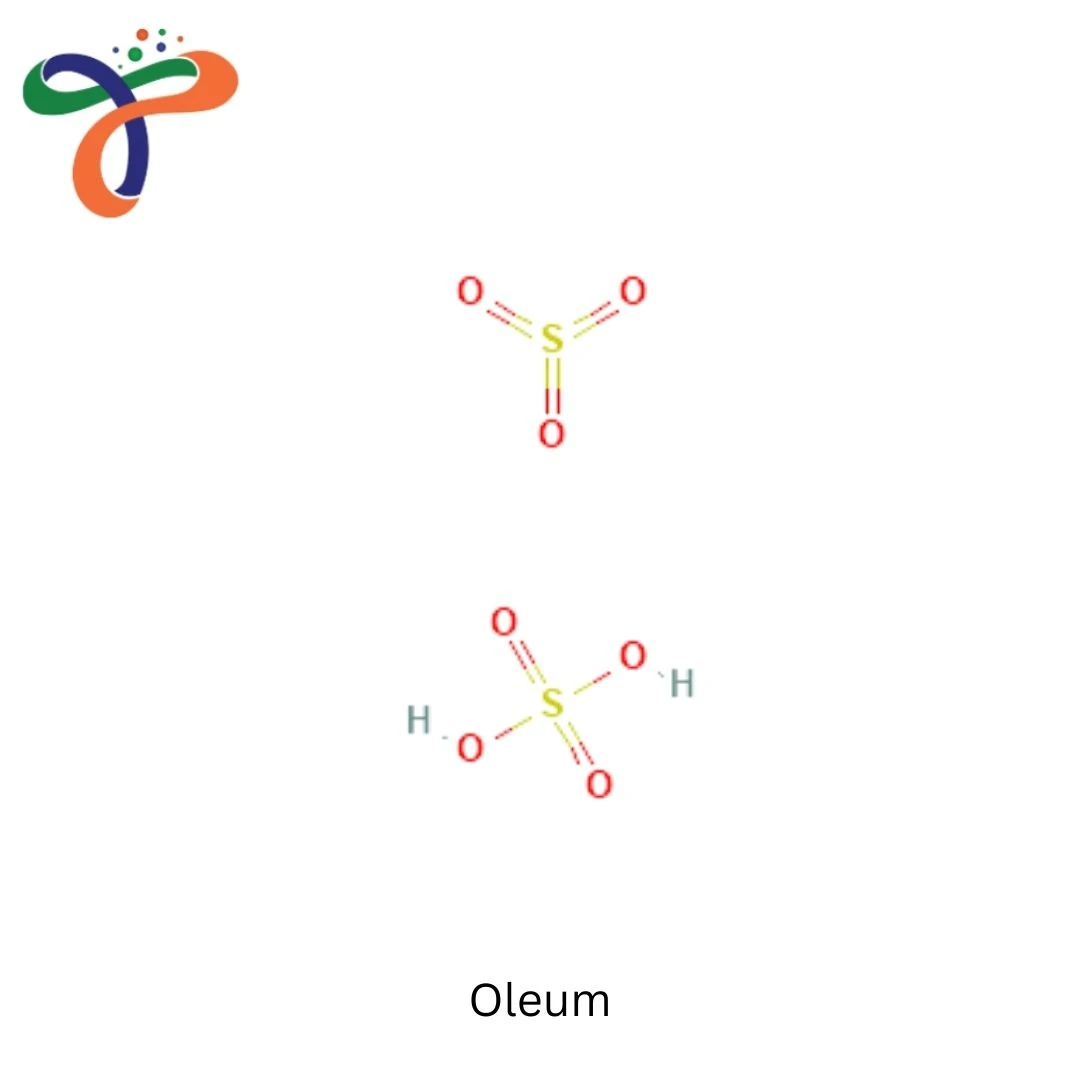
Molecular Formula :
H2SO4.SO3
Boiling Point :
338 °C
Melting Point :
-5 °C
Flash Point :
300 °C
Solubility :
Reacts Violently With Water; Miscible With Water
Description :
Overview of Oleum
Oleum, also known as fuming sulphuric acid, is a highly concentrated form of sulphuric acid containing dissolved sulphur trioxide (SO₃). Chemically, the oleum formula is commonly represented as H₂S₂O₇, though it is more accurately described as a solution of SO₃ in sulphuric acid. The oleum chemical formula and structure vary depending on the free SO₃ content, which defines different commercial grades used in industrial processes.
From a structural perspective, the oleum structure consists of sulphuric acid molecules associated with sulphur trioxide, forming disulphuric acid. The oleum formula and structure explain its strong dehydrating and sulphonating properties, making it a critical reagent in heavy chemical industries. Oleum appears as a colourless to slightly brown fuming liquid, emitting dense white fumes due to moisture absorption from the air.
Due to its high reactivity, oleum uses are primarily industrial, particularly where concentrated sulphuric acid strength is insufficient. ChemicalBull supplies industrial-grade Oleum with controlled SO₃ concentration, consistent quality, and safe logistics support. Each supply batch is backed by complete technical documentation, including MSDS, COA, and handling guidelines, ensuring safe industrial application.
As a trusted chemical supplier and reliable distributor, ChemicalBull supports large-scale chemical manufacturing across sectors. You may also like Nitric Acid and Phosphoric Acid for related industrial acid and sulphonation applications available on our site.
Applications of Oleum
Sulphonation & Chemical Manufacturing
-
Used extensively for sulphonation and nitration reactions
-
Essential in detergent, dye, and pigment manufacturing
-
Enables controlled chemical transformation processes
Explosives & Speciality Chemicals
-
Used in the production of explosives and energetic materials
-
Supports synthesis of high-purity speciality intermediates
-
Suitable for regulated industrial environments
Petroleum & Refining Industry
-
Applied in refining and hydrocarbon processing
-
Used for acid treatment and purification steps
-
Enhances process efficiency in chemical refining
Fertiliser & Inorganic Chemical Production
-
Used in manufacturing sulphate-based chemicals
-
Acts as a strong dehydrating agent in inorganic synthesis
-
Supports large-scale industrial chemical plants
Safety & Handling Guidelines
-
Handle only with acid-resistant gloves, face shields, and protective clothing
-
Avoid direct contact with moisture and organic materials
-
Use in corrosion-resistant equipment and controlled environments
-
Store in tightly sealed containers away from water sources
-
Strictly follow MSDS and industrial acid handling standards
Where to Buy Oleum?
Oleum Manufacturer
ChemicalBull supplies high-purity Oleum for sulphonation, chemical processing, and heavy industrial applications.
Oleum Supplier & Distributor
-
Available in bulk and customised industrial packaging
-
Export-quality material with COA, TDS & MSDS
-
Reliable supply across India and global markets
-
Trusted chemical supplier for strong acids and industrial reagents
Oleum MSDS
The Oleum MSDS contains critical safety information regarding handling precautions, storage requirements, exposure limits, spill response, and emergency procedures. Reviewing the MSDS before industrial use is mandatory for safe operation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the chemical formula of Oleum?
The oleum chemical formula is commonly written as H₂S₂O₇, though it represents sulphuric acid containing dissolved sulphur trioxide. -
How is the Oleum structure different from sulphuric acid?
The oleum structure includes additional SO₃ molecules bonded within sulphuric acid, giving it stronger dehydrating and sulphonating properties. -
What is the molecular weight of Oleum?
The oleum molecular weight for disulphuric acid (H₂S₂O₇) is approximately 178.14 g/mol, though commercial oleum varies based on SO₃ concentration. -
What are the main industrial uses of Oleum?
Key oleum uses include sulphonation reactions, dye and detergent manufacturing, explosives production, and petroleum refining. -
Why is Oleum preferred over concentrated sulphuric acid?
Oleum is used when higher acidity or controlled SO₃ content is required, making it more effective for specific industrial chemical reactions.