Diphenylamine | 122-39-4
Cas No :
122-39-4
Form :
Solid
Molecular Weight :
169.23
Molecular Formula :
C12H11N
Melting Point :
50 - 53 °C
Boiling Point :
302 °C
Solubility :
Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly)
Description :
Overview of Diphenyl Amine
Diphenyl Amine can be described as an industrial aromatic amine compound commonly employed in processes of manufacturing in which the control of oxidation, stabilisation and consistency in the performance of aromatic amines are needed. It is usually supplied in the form of a pale to white crystallised solid that might be slightly darker upon exposure to air. Diphenyl Amine is appreciated for its antioxidant properties, chemical stability as well as its reliable performance when used in formulations that are industrial.
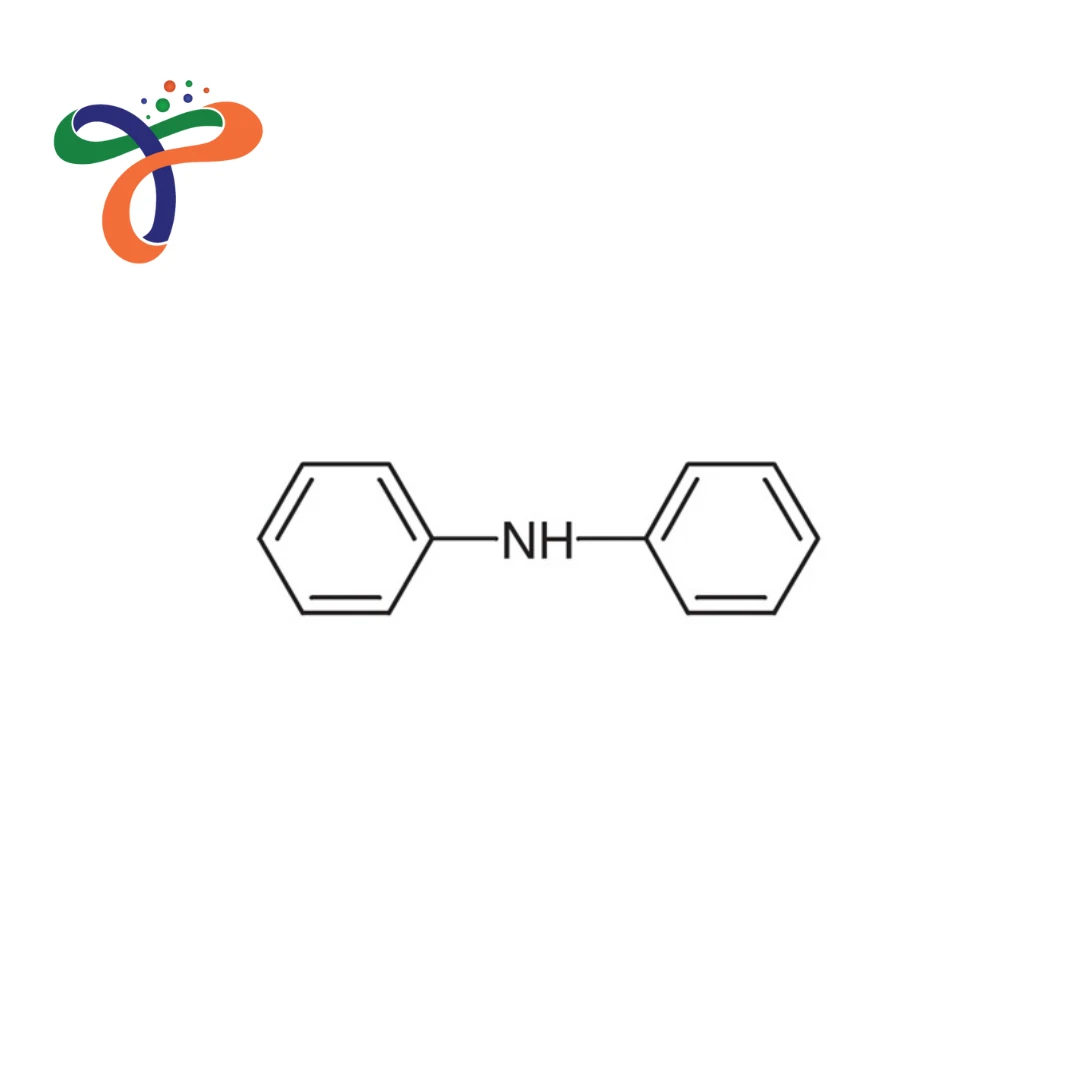
Diphenylamine is known in chemical nomenclature by its IUPAC name N-phenylaniline and is commonly used as an industrial stabiliser, intermediate, and analytical reagent.
Applications of Diphenyl Amine
Antioxidant & Stabiliser Applications
Diphenylamine is used extensively to act as an antioxidant and a stabiliser in industrial processes where prevention of oxidation is crucial. It protects substances from oxidative and thermal degradation and extends the duration of service for industrial formulations. It is usually evaluated with butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) for stability performance.
Chemical Manufacturing & Industrial Intermediates
Diphenyl Amine is a key alternative in manufacturing, where aromatic amines are required for subsequent reactions. It permits the controlled synthesis process and ensures constant batch quality. It could be compared to the chemical Aniline in the field of aromatic chemical chemistry.
Analytical & Indicator Applications
Diphenylamine is utilised as a marker in analytical chemistry because of its colour change in reactions of oxidation. This makes it suitable for industrial and laboratory quality control tests. It is often used along with Diphenylamine Sulfonate to make analytical equipment.
Safety & Handling Guidelines
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
- Keep containers tightly sealed and protected from light
- Avoid inhalation of dust during handling
- Avoid prolonged contact with skin and eyes
- Use protective gloves, goggles, and suitable industrial clothing
- Maintain proper ventilation during processing
- Dispose of material and packaging as per local regulations
Where to Buy Diphenyl Amine?
Diphenyl Amine Manufacturer
Diphenyl Amine is manufactured for industrial applications where consistent purity, controlled aromatic amine content, and reliable stabilising performance are required.
Diphenyl Amine Supplier & Distributor
Diphenyl Amine is available in industrial-grade quantities to manufacturers who require dependable quality and a steady supply. As a leading industrial chemicals distributor, Chemicalbull Pvt. Ltd. assists customers by providing solid sourcing and standard documents for industrial needs.
MSDS for Diphenyl Amine
MSDS for Diphenyl Amine contains specific information about hazards, as well as safe handling methods, the storage environment, exposure control, first-aid measures, and guidelines for emergency response. Always read the MSDS prior to use in industrial settings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the IUPAC name of Diphenyl Amine?
The IUPAC name of Diphenyl Amine is N-phenylaniline. -
What is the structure of Diphenylamine?
Diphenylamine structure consists of two phenyl rings bonded to a central amine (–NH–) group, giving it aromatic amine characteristics. -
What is the colour of Diphenylamine?
Diphenylamine is typically white to pale crystalline in colour and may darken slightly upon exposure to air. -
What is Diphenyl Amine used for?
Diphenyl Amine is used as an antioxidant, stabiliser, chemical intermediate, rubber additive, and analytical indicator in industrial applications. -
Why is Diphenylamine used as an indicator?
Diphenylamine is used as an indicator because it undergoes a distinct colour change during oxidation reactions, making it useful in analytical and quality control processes.