Phenol | 108-95-2
Cas No :
108-95-2
Synonyms :
Form :
Liquid
Molecular Weight :
94.11 G/Mol
Molecular Formula :
C₆H₆O
Boiling Point :
181.7 °C
Melting Point :
40.5 °C
Flash Point :
79 °C
Solubility :
8.3 G/100 Ml Water At 20 °C
Description :
Overview of Phenol
Phenol is an essential aromatic organic compound that is widely utilized as a major ingredient in chemicals, pharmaceuticals, resins, polymers, and chemical industries. It is a transparent, translucent, or pale pink solid that is well-known by its distinctive phenolic smell and its high chemical reactivity.
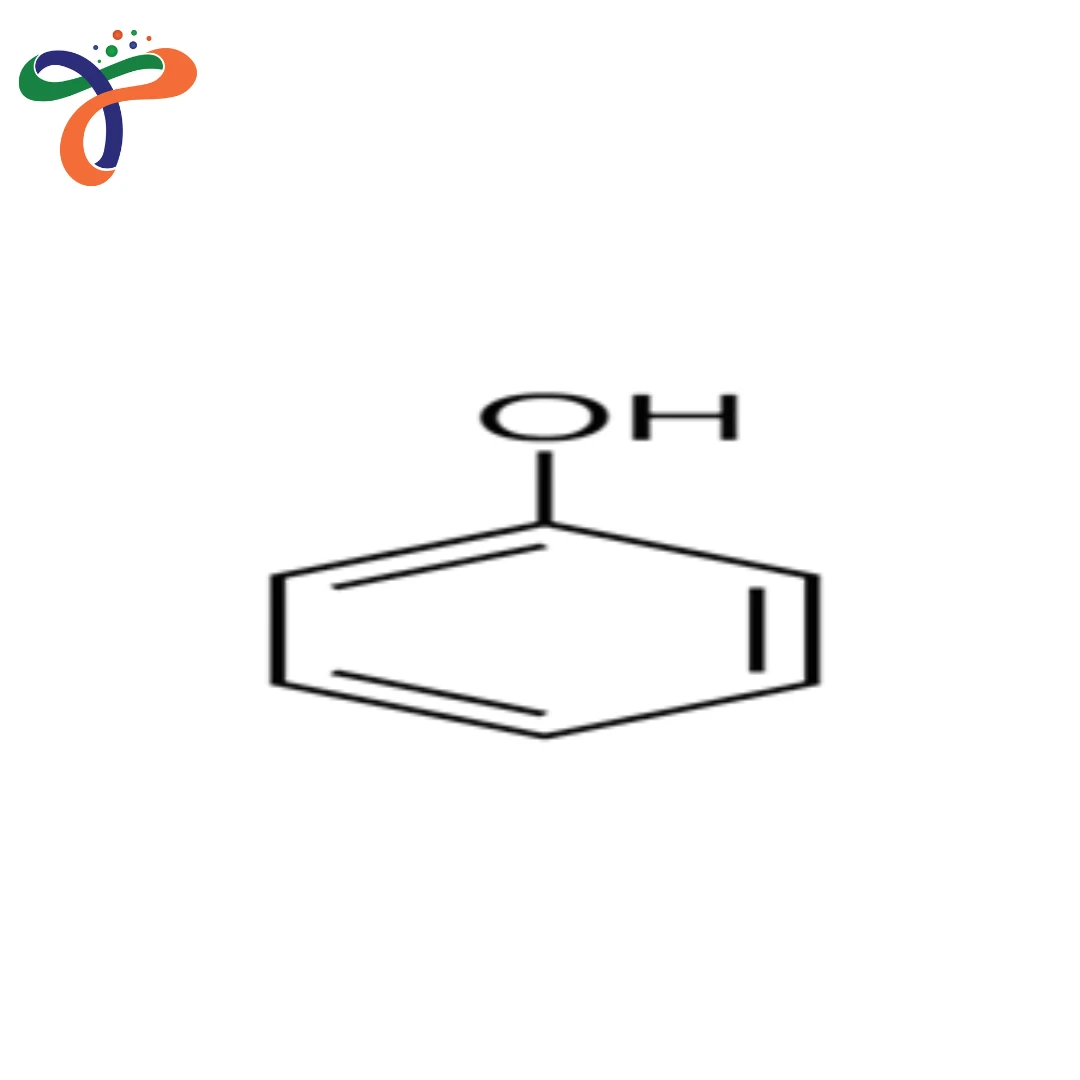
The formula for phenol is C6H5OH. The structure of the phenol consists of the hydroxyl group directly attached to a benzene ring, giving the phenol its acidic as well as reactive nature. Because of its plethora of chemical behaviors, phenol is widely used as a precursor for industrial intermediates and specialty chemicals.
In the industrial world, phenol is made by a variety of routes. The most common way to explain the process of making phenol is using chlorobenzene and an alkaline hydrolysis process at high temperatures and pressure. Another common transformation in organic chemistry concerns the conversion of aniline to phenol. This happens through diazotisation and then hydrolysis. These reactions reveal phenol's crucial function in the field of aromatic chemical chemistry.
Applications of Phenol
Chemical & Industrial Manufacturing
- Used as a core raw material for phenolic resins, epoxy resins, and polycarbonates
- Acts as a precursor in the synthesis of bisphenol-A, caprolactam, and alkyl phenols
- Essential intermediate in dyes, plastics, and agrochemical formulations
Pharmaceutical Applications
- Used in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates
- Acts as a disinfectant and antiseptic in controlled concentrations
- Supports the formulation of analgesics and antiseptic compounds
Laboratory & Research Applications
- Used as a reagent in organic synthesis and analytical chemistry
- Important compound for studying aromatic substitution reactions
- Demonstrates reactions such as the conversion of aniline to phenol and chlorobenzene to phenol
Industrial & Specialty Chemical Processing
- Used in the production of surfactants, antioxidants, and plastic additives
- Applied in specialty chemical formulations and controlled industrial reactions
- Can be used in combination with Monocalcium Phosphate Anhydrous, Monoethylene Glycol, and Morpholine for specialised chemical and formulation processes
Safety & Handling Guidelines
- Toxic and corrosive Be sure to handle it with care
- Use chemical-resistant gloves or goggles and wear safety clothes
- Avoid contact with the skin or breathing in volatiles
- Only use in ventilated locations or in fume Hoods
- Keep in sealed containers far from oxidising agents and heat
- Be sure to follow MSDS and the industrial safety rules completely
Where to Buy Phenol?
Phenol Manufacturer
ChemicalBull supplies high-quality Phenol suitable for industrial, pharmaceutical, and laboratory applications with assured purity and consistency.
Phenol Supplier & Distributor
- Bulk and customised packaging options available
- Export-grade material with COA, TDS & MSDS
- Reliable supply for chemical manufacturers, research labs, and industrial users
Explore related products: Monocalcium Phosphate Anhydrous, Monoethylene Glycol, Morpholine
Phenol MSDS
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provides detailed information on health hazards, safe handling practices, storage conditions, and emergency measures. Always review the MSDS before using phenol in any application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is phenol used for?
Phenol is used in resins, plastics, pharmaceuticals, dyes, surfactants, and chemical synthesis. -
What is the chemical formula of phenol?
The phenol formula is C₆H₅OH. -
How is phenol prepared from chlorobenzene?
Phenol is prepared by hydrolysis of chlorobenzene using sodium hydroxide at high temperature and pressure, followed by acidification.