Hydroiodic Acid | 10034-85-2
Cas No :
10034-85-2
Form :
Liquid
Molecular Weight :
127.91 G/Mol
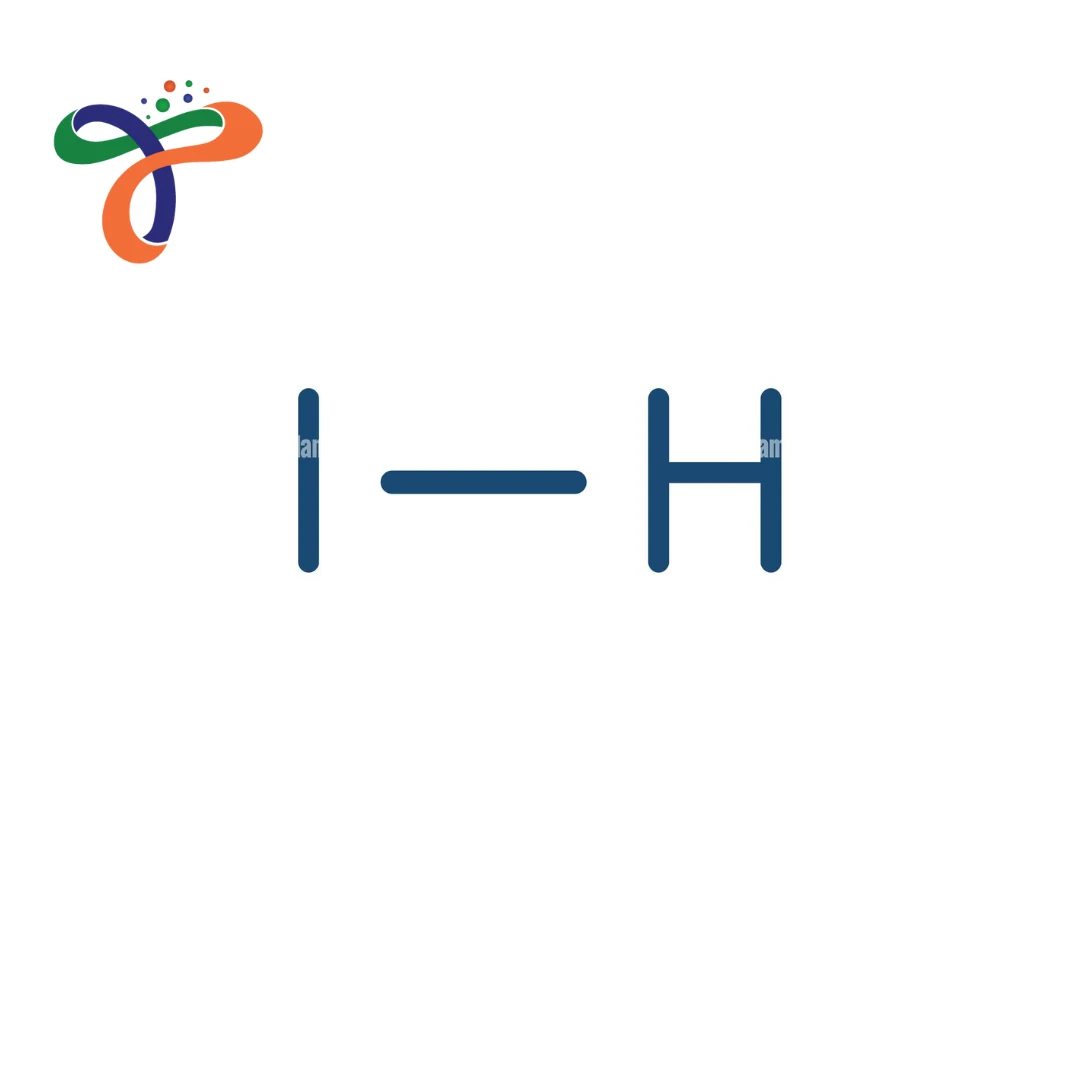
Molecular Formula :
HI
Melting Point :
-50 °C
Boiling Point :
-34 °C
Solubility :
Miscible With Water
Flash Point :
-23 °C
Description :
Overview of Hydroiodic Acid
Hydroiodic Acid is a strong industrial inorganic acid widely used in manufacturing processes where high acidity, strong reducing ability, and controlled iodide chemistry are required. It is typically supplied as a clear, colourless to pale yellow aqueous solution and is valued for its high reactivity, consistent concentration, and reliable performance in industrial chemical processing.
Hydroiodic Acid is commonly recognised as one of the strongest hydrohalic acids, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient cleavage, reduction, and iodide incorporation under controlled conditions.
Applications of Hydroiodic Acid
Chemical Manufacturing & Industrial Synthesis
Hydroiodic Acid is extensively used in chemical manufacturing where strong acid conditions and iodide ions are required for reduction, substitution, and cleavage reactions. It supports predictable reaction pathways and consistent batch performance. It is often evaluated alongside Hydrochloric Acid and Hydrobromic Acid depending on process requirements.
Reduction & Cleavage Processes
Hydroiodic Acid is used in industrial reduction processes where it acts as a powerful reducing agent. It supports controlled deoxygenation and bond cleavage in specialised industrial reactions.
Iodide Salt & Intermediate Production
Hydroiodic Acid is used in the production of iodide salts and iodine-containing intermediates where controlled iodide concentration and purity are essential. It may be processed alongside Potassium Iodide and Sodium Iodide in iodide chemistry.
Specialty Industrial Processing
Hydroiodic Acid is also used in specialty industrial applications where strong acidity and reliable iodide chemistry are required for process efficiency and product consistency.
Safety & Handling Guidelines
-
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
-
Use corrosion-resistant containers and equipment
-
Avoid inhalation of vapours and direct contact with skin or eyes
-
Use protective gloves, goggles, face shield, and suitable industrial clothing
-
Handle under controlled industrial conditions due to strong corrosivity
-
Keep away from oxidising agents and incompatible materials
-
Dispose of waste and containers according to regulatory guidelines
Where to Buy Hydroiodic Acid?
Hydroiodic Acid Manufacturer
Hydroiodic Acid is manufactured for industrial applications where controlled concentration, consistent strength, and reliable performance are required for chemical synthesis and iodide-based processing.
Hydroiodic Acid Supplier & Distributor
Hydroiodic Acid is supplied in industrial-grade packaging to manufacturers requiring dependable quality and regulated handling. As an industrial chemicals supplier and distributor, Chemicalbull Pvt. Ltd. supports customers with reliable sourcing and standard documentation.
MSDS for Hydroiodic Acid
The MSDS for Hydroiodic Acid provides detailed information on hazards, safe handling procedures, storage conditions, exposure controls, first-aid measures, and emergency response protocols. Always review the MSDS before industrial use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Is HI Hydroiodic Acid?
Yes, HI is the chemical formula for Hydroiodic Acid when hydrogen iodide is dissolved in water. -
What is the structure of Hydroiodic Acid?
Hydroiodic acid structure consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to an iodine atom (H–I) in aqueous solution. -
What is the common name for Hydroiodic Acid?
The common name for Hydroiodic Acid is hydrogen iodide solution. -
What are the uses of Hydroiodic Acid?
Hydroiodic Acid is used in chemical synthesis, reduction reactions, iodide salt production, and specialty industrial processing. -
What happens when Hydroiodic Acid reacts with Potassium Hydroxide?
Hydroiodic acid and potassium hydroxide react to form potassium iodide (KI) and water in a neutralisation reaction.