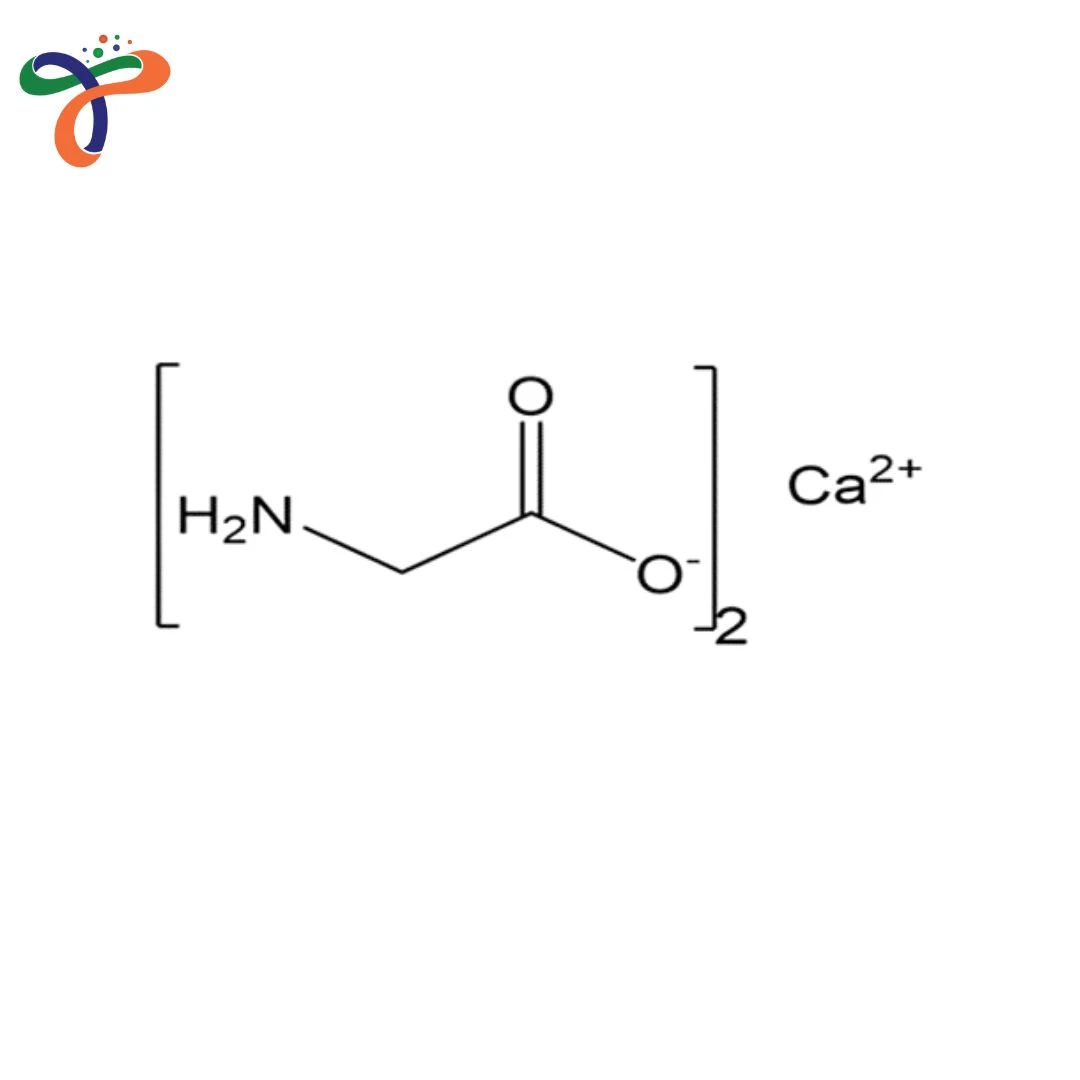
Calcium Bisglycinate | 35947-07-0
Cas No :
35947-07-0
Form :
Powder
Molecular Weight :
188.20 G/Mol
Molecular Formula :
C4H8CAN2O4
Melting Point :
170 °C
Boiling Point :
860 °C
Solubility :
Freely Soluble In Water; Soluble In Ethanol
Flash Point :
300 °C
Description :
Overview of Calcium Bisglycinate
Calcium Bisglycinate is a pharmaceutical-grade chelated calcium compound formed by binding calcium with two glycine molecules. This chelated structure improves stability, absorption, and gastrointestinal tolerance compared to many conventional calcium salts.
In pharmaceutical and nutritional formulations, Calcium Bisglycinate is valued for its high bioavailability, gentle digestion profile, and suitability for long-term supplementation. Its amino acid chelation supports consistent calcium delivery under regulated manufacturing conditions.
As a pharmaceutical chemical, Calcium Bisglycinate is widely used in advanced calcium supplements and combination mineral formulations.
Applications of Calcium Bisglycinate
Pharmaceutical & Nutritional Supplements
Calcium Bisglycinate is commonly used in calcium supplements formulated for improved absorption and reduced gastrointestinal discomfort. It is often preferred over traditional salts in products designed for sensitive users.
In comparative formulations, it is frequently evaluated alongside Calcium Citrate Malate and Calcium Gluconate to assess bioavailability and formulation performance.
Pharmaceutical Formulation & Mineral Complexes
In pharmaceutical formulation, Calcium Bisglycinate is used in multi-mineral and amino acid–based supplements where compatibility and stability are essential. Its chelated nature allows efficient absorption without competing strongly with other dietary minerals.
It is also compared with Magnesium Glycinate in chelated mineral systems designed for enhanced tolerability.
Clinical Nutrition & Supplement Development
Calcium Bisglycinate supports clinical nutrition products aimed at bone health and mineral balance. Compared to calcium carbonate, it generally offers better absorption and does not require high stomach acid levels for effective uptake.
Safety & Handling Guidelines
-
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
-
Keep containers tightly sealed and clearly labelled
-
Avoid excessive dust formation during handling
-
Avoid direct contact with eyes and prolonged skin exposure
-
Use protective gloves, goggles, and suitable pharmaceutical-grade clothing
-
Handle under controlled pharmaceutical manufacturing conditions
-
Dispose of waste according to regulatory guidelines
Where to Buy Calcium Bisglycinate?
Calcium Bisglycinate Manufacturer
Calcium Bisglycinate is manufactured for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications where high purity, consistent chelation, and formulation reliability are required.
Calcium Bisglycinate Supplier & Distributor
Calcium Bisglycinate is supplied in pharmaceutical-grade packaging for supplement manufacturers and healthcare product producers. As a pharmaceutical chemicals supplier and distributor, Chemicalbull Pvt. Ltd. supports customers with reliable sourcing and standard documentation.
MSDS for Calcium Bisglycinate
The MSDS for Calcium Bisglycinate provides detailed information on handling precautions, storage conditions, exposure controls, first-aid measures, and safety guidelines. Always review the MSDS before pharmaceutical or nutritional use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Is Calcium Bisglycinate the same as Calcium Glycinate?
Yes, Calcium Bisglycinate is commonly referred to as Calcium Glycinate, as both describe calcium chelated with glycine for improved absorption. -
Is Calcium Bisglycinate better than Calcium Citrate?
Calcium Bisglycinate is often considered better tolerated and more bioavailable than calcium citrate, particularly for individuals with sensitive digestion. -
What is the structure of Calcium Bisglycinate?
Calcium Bisglycinate structure consists of a central calcium ion chelated by two glycine molecules, forming a stable amino acid complex.