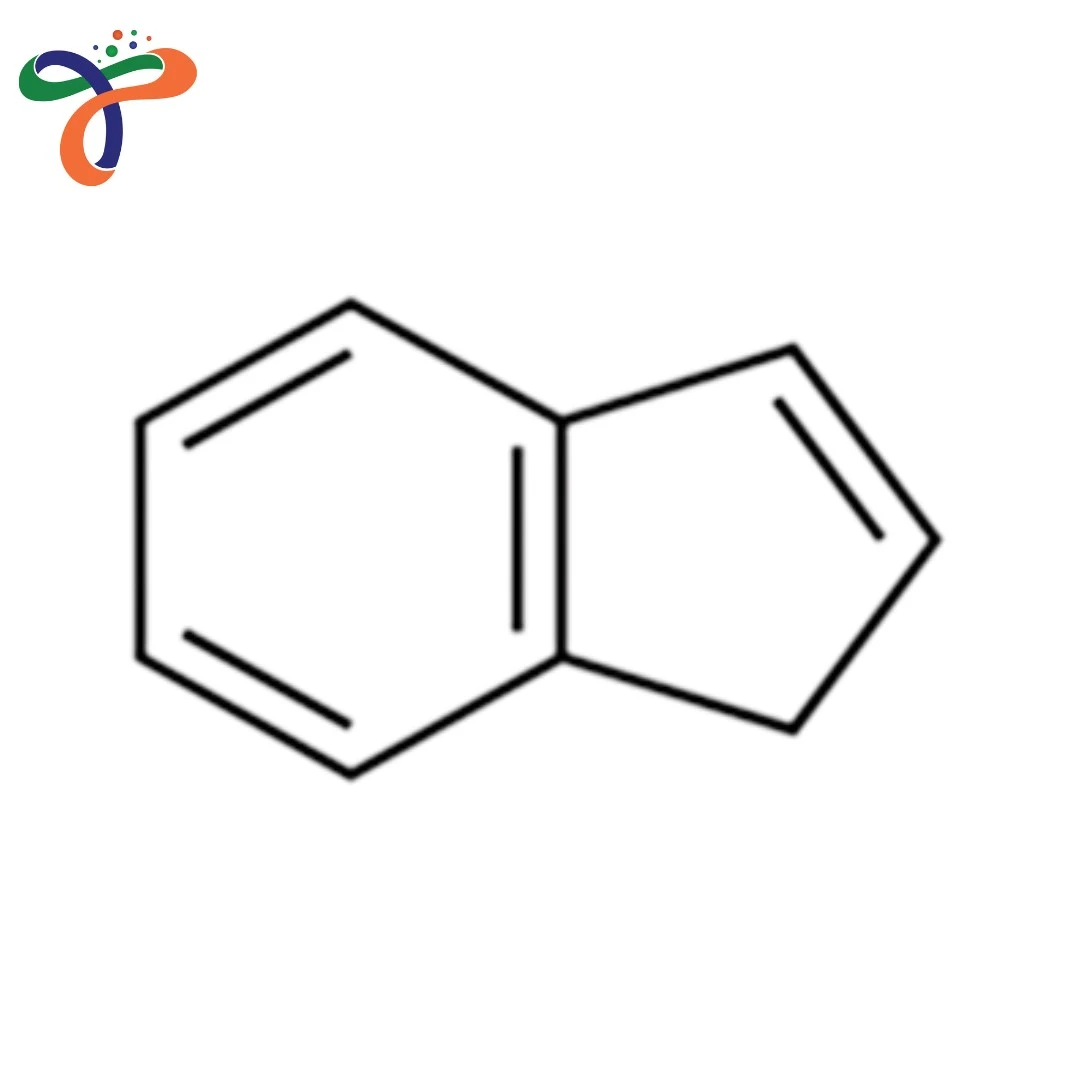
Indene | 95-13-6
Cas No :
95-13-6
Synonyms :
Form :
Liquid
Molecular Weight :
116.16
Molecular Formula :
C9H8
Boiling Point :
181 - 182 °C
Melting Point :
5 - -3 °C
Flash Point :
58 °C
Solubility :
Insoluble In Water, Partially Soluble In Organic Solvents
Description :
Overview of Indene
Indene is a colorless to faint yellow liquid with an aromatic odor. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, C9H8, consisting of an indane and styrene type. Derived from coal tar or petroleum distillates, indene is a chemical intermediate regularly needed for the manufacture of resins, polymers, and fine chemicals. Indene's reactivity and versatility make it a useful key raw material in the manufacture of synthetic resins, coatings, and fragrance intermediates. Indene's derivatives are often used in laboratory, industrial, and polymer-related applications.
Applications of Indene
Chemical & Industrial Applications
Indene is primarily used in the production of indene-coumarone resins, which are applied in paints, coatings, varnishes, and adhesives. These resins enhance durability, gloss, and adhesion in industrial coatings. Indene is also used as a monomer and polymer additive in the manufacturing of plastics and synthetic rubbers. Explore related fine chemicals like Phytol and Vinyl Sulfurol.
Fragrance & Perfumery uses
Indene and its derivatives are commonly employed in aroma chemical synthesis as intermediates and contribute to woody, amber, and balsamic aspects of perfumery molecules. It is often utilised in synthetic musk bases, resinous fragrance compositions, and can lend depth and fixative qualities to a fragrance. Related fragrance ingredients include Rosalva and Linalyl Formate.
Research & Laboratory Use
In research and academic chemistry, Indene is used as a starting material in organic synthesis, catalysis studies, and polymer research. Its conjugated structure makes it helpful in studying aromatic reactivity and polymerization mechanisms. You may also like Fenchyl Alcohol and Octyl Palmitate.
Speciality & Intermediate Applications
Indene is an important building block in the production of fine chemicals, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. Its structure allows for easy functionalization, leading to compounds used in pharmaceutical intermediates and advanced materials. Explore other intermediates such as Ethyl Isovalerate and Pentanoic Acid.
Safety & Handling Guidelines
-
Always wear protective gloves, goggles, and chemical-resistant clothing when handling.
-
Avoid inhalation and direct contact with skin or eyes.
-
Handle in a well-ventilated workspace or under a fume hood.
-
Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, dry, and dark location, away from open flames and oxidizing agents.
-
Dispose of waste material in compliance with local environmental and safety regulations.
Where to Buy Indene?
Indene Manufacturer
ChemicalBull manufactures and supplies high-quality Indene suitable for industrial, chemical, and research applications. Each batch is tested for purity, composition, and stability to ensure consistent performance.
Indene Distributor & Supplier
We supply Indene in bulk and custom-packaged quantities, delivered promptly with technical support and regulatory compliance for multiple industries.
Indene MSDS
Request the official Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for comprehensive information on handling, toxicity, and environmental impact of Indene from ChemicalBull.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Where can I buy Indene?
You can buy high-quality Indene directly from ChemicalBull, a trusted manufacturer and supplier of hydrocarbon intermediates and fine chemicals in India. -
Is Indene safe to use?
Indene is safe when used under recommended industrial conditions. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are essential due to its flammability and aromatic vapour. -
What is a synonym for Indene?
Common synonyms for Indene include 1H-Indene, -
What does Indene smell like?
Indene has a mild aromatic odour, often described as sweet, resinous, and tar-like, characteristic of hydrocarbon derivatives.