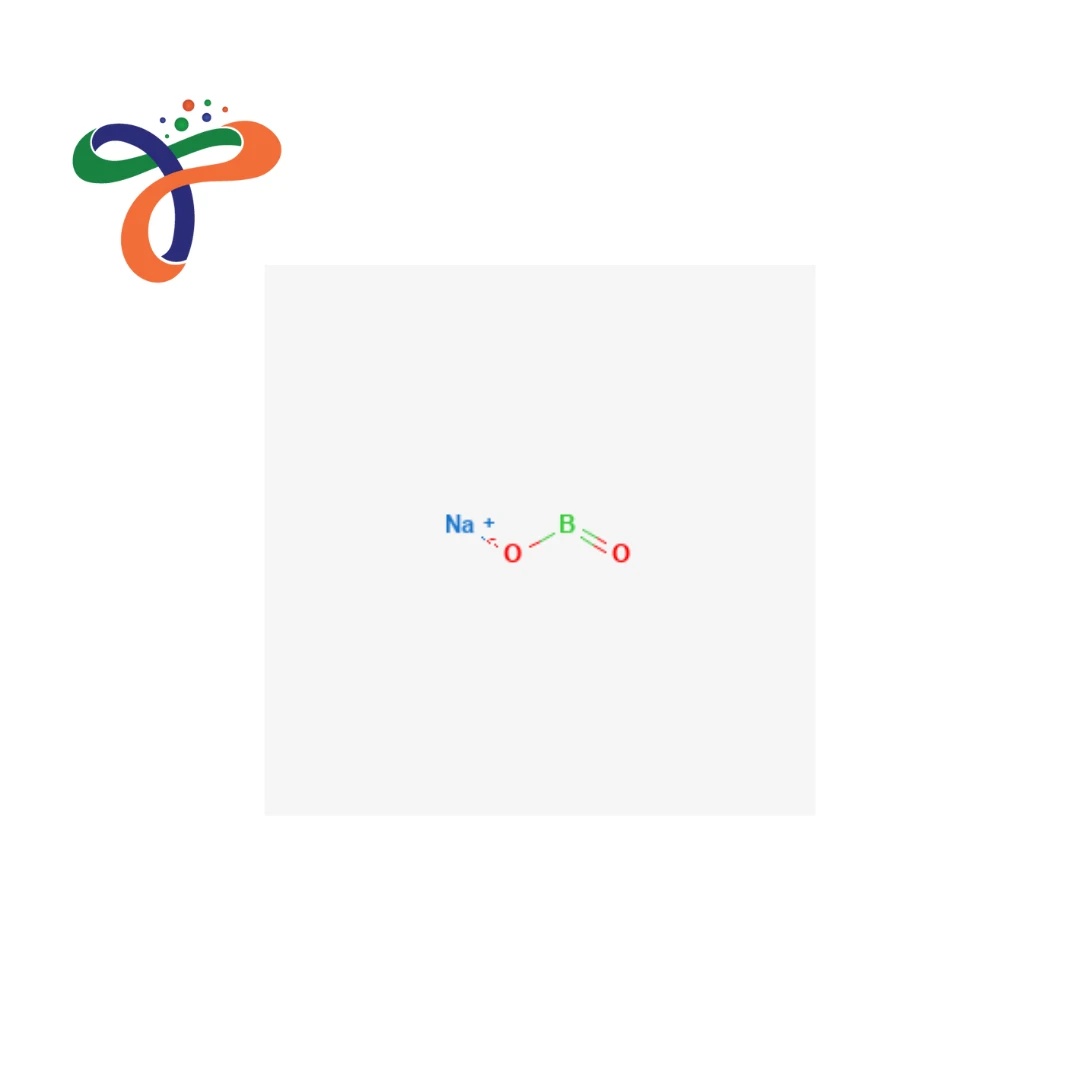
Colemanite
Form :
Powder
Molecular Weight :
195.3 G/Mol
Molecular Formula :
B4CAO7
Description :
Overview of Colemanite
Colemanite is an industrial borate mineral widely utilised in manufacturing processes that demand consistent boron content, thermal stability, and raw material performance. As an important source of boron, it has numerous industrial applications such as glass making, ceramic production, metallurgical processing, and many others. Colemanite stands out for its stable chemistry that ensures reliable high-temperature performance as well as suitable use in formulations requiring controlled boron inputs.
Colemanite structure is based on calcium borate hydrate composition, which supports its performance as an industrial boron mineral.
Applications of Colemanite
Glass & Ceramic Manufacturing
Colemanite is widely utilised in glass and ceramic production where its boron minerals support controlled melting behaviour, improved thermal stability and long product durability. Colemanite helps ensure consistent processing output and quality throughout industrial production - often used with Boron Oxide, depending on requirements for its boron content.
Metallurgy & Flux Applications
Colemanite is used in metallurgy where it supports flux action, impurity removal, and stable metal processing performance. It helps improve processing efficiency and supports consistent output quality. It may be handled with Borax Anhydrous depending on industrial flux requirements.
Industrial Chemical Processing
Colemanite is used in industrial chemical processing where borate minerals support stable formulation behaviour and consistent boron-based performance. It supports controlled processing conditions and reliable manufacturing output.
Speciality Industrial Formulations
Colemanite can also be used in speciality industrial formulations that call for consistent raw material quality and boron mineral performance, offering stable industrial output and manageable processing behaviours.
Safety & Handling Guidelines
-
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
-
Keep containers tightly sealed and protected from moisture
-
Avoid inhalation of fine dust during handling
-
Avoid direct contact with the eyes
-
Always wear protective gloves, goggles and clothing when processing Colemanite
-
Maintain proper dust control during processing
-
Dispose of residues and packaging as per local regulations
Where to Buy Colemanite?
Colemanite Manufacturer
Colemanite is processed and supplied for industrial applications where consistent boron content, stable quality, and reliable performance are required for glass, ceramics, metallurgy, and chemical processing industries.
Colemanite Supplier & Distributor
Chemicalbull Pvt Ltd offers industrial-grade quantities of Colemanite for manufacturers who demand consistent quality and steady supplies. As an industrial chemicals supplier and distributor, Chemicalbull provides customers with reliable sourcing support as well as documentation tailored to industrial standards.
MSDS for Colemanite
Colemanite Material Safety Data Sheets provide thorough information regarding safe handling, storage conditions, exposure controls, first aid measures and emergency response protocols. Please review them prior to industrial use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the chemical formula of Colemanite?
Colemanite formula is commonly written as Ca₂B₆O₁₁·5H₂O. -
What is the structure of Colemanite?
One alternative name for colemanite is calcium borate mineral. -
What is colemanite used for?
Colemanite is used in glass and ceramic manufacturing, metallurgical flux applications, fertiliser processing, and industrial chemical formulations requiring boron minerals. -
What is another name for colemanite?
Another name for colemanite is calcium borate mineral (commonly referred to in industrial borate raw material categories). -
What is a substitute for colemanite?
A substitute for colemanite depends on the application, but common alternatives include Borax Anhydrous, Boric Acid, and Boron Oxide, based on boron content and process requirements.